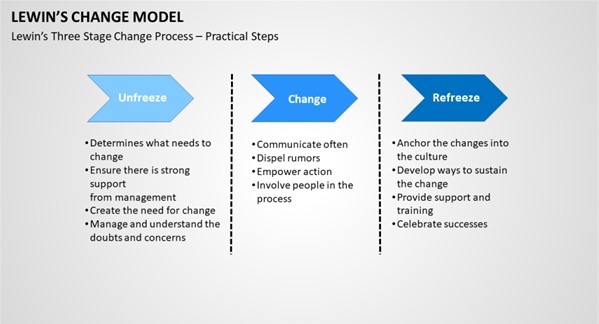
The style of leadership that I vision of becoming is a situational leader designed by Hersey and Blanchard. Based on blog 3, this approach analyzes different leadership situations to attain the best outcome. After going through the various styles of leadership, situational leadership suits my preference as it is flexible and easily adaptable. According to Abudi (2012), everyone is unique from each other and leaders should determine a particular style of leadership based on the types of groups they manage. Notably, based on the experiences that I had with my superior, I was comfortable being led by him and observed that he used the situational approach to guide subordinates instead of just delegating tasks.
Johari window

Figure 1: Johari Window hidden personality dimension
Leaders should encourage their subordinate to unmask their hidden personality and expose their strength and weakness using the Johari Window dimension (Hamzah et al. 2016). This model is recommendable as I manage to identify my strengths and weakness which will aid me in assisting my colleagues to unleash their hidden potential through the tasks assigned.
Leader that inspired me- Jeff Wiener (CEO of LinkedIn)

Figure 2: Jeff Wiener (CEO of LinkedIn)
The leader who inspired my thoughts on leadership was Jeff Wiener; currently the CEO of LinkedIn which is a professional social networking site. The company gained more than 530 million users as of 2017 and the workforce size boomed from 338 to over 11000 employees globally (CBS News 2017). Since Wiener became the CEO of LinkedIn in 2008, he obtained a large fan base among employees and is a highly rated CEO having what it takes to be a successful leader without being selfish in sharing knowledge with others (Friedman 2017). Besides, Wiener demonstrated that between ‘Leaders or Managers’, managers instruct tasks whereas leaders inspire based on the clarity of vision, conviction and effective communication (Friedman 2017). Moreover after analyzing his style, I truly admire his authenticity and clear communication which makes me more interested to understand LinkedIn’s working culture and practices. His leadership style that upholds guidance rather than managing employees has contributed to the growth of the company.
Am I ready to lead?

Based on feedbacks received from my colleagues, my strength significantly leaned on enabling others which reflects my current character as I am able to relate, listen and support others which indirectly boosted my confidence. Besides, I realized that I would need to improve my encouraging skills as it is important for leaders to motivate their subordinates to steer them in the right direction which is my upcoming 3-year plan in my current industry. Moreover, challenge and inspire units are needed equally for me to enhance myself in the future. I would need to read more leadership materials and attend events to indulge myself with the communities around me to develop change and improve my leadership traits.

Based on the 16 personality test, I realized that the comments made by colleagues were close to an executive (ESTJ-A). According to Burke (2019), traits of an executive is one who understands and able to discern between right and wrong while giving clear advice and guidance to others. This trait is one that closely defines my character.
Leadership skills that I want to develop as I progress through MBA
As I progress through MBA, I would want to further enhance the following leadership skills such as communication, motivating, positivity and responsibility. Firstly, communication skills would be through the group assignments and presentations of reports. Secondly, motivating skills are vital as it aids in supporting teammates to persevere during stressful periods of the course and also in projects at the workplace. Through this, it will enable me to achieve my personal goals and attain satisfaction in the tasks. Notably, I would further enhance my positivity skill as it is important to remain positive during all times to ensure a good relationship between members at my MBA course and workplace. Lastly, responsibility skills are crucial as a leader in times of success or failure and it is important to analyze situations and derive solutions accordingly without blaming others. With these skills, I will be able to achieve my personal goals and become a good leader.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, upon analyzing and reflecting on my strength and weaknesses, there are steps and measures which are necessary to ensure my leadership skills are fulfilled such as volunteering to lead activities and participating in talks. With the extra knowledge gained, I hope to achieve my dream of leading a team of my own in the near future.
(766 Words)
Reference
CBS NEWS. (2017) ‘Linkedin CEO Jeff Weiner on compassionate leadership importance of protecting “Dreamers” CBSNEWS [online] 11th October Available from <https://www.cbsnews.com/news/linkedin-ceo-jeff-weiner-leadership-daca/> [18 March 2019].
Abudi, G. (2012) ‘Tailoring your leadership style to your employees’. [online]. Available from <https://www.ginaabudi.com/tailoring-your-leadership-style-to-your-employees/> [13th March 2019].
Hamzah, M. I., Othman, A. K., Hassan, F., Razak, N.A., Yunus, N.A.M (2016) ‘Conceptualizing a schematic Grid view of customer knowledge from the johari windows perspective’ Faculty of Business and Management. 37 471-479. [Online]. Available from <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221256711630154X> [18 March 2019].
16Personalities. (2019) ‘The Executive’ [online] available from < https://www.16personalities.com/free-personality-test> [18 March 2019].
Burke, E. (2019) ‘Executive Personality (ESTJ, -A/-T)’ [online] available from < https://www.16personalities.com/estj-personality> [18 March 2019].